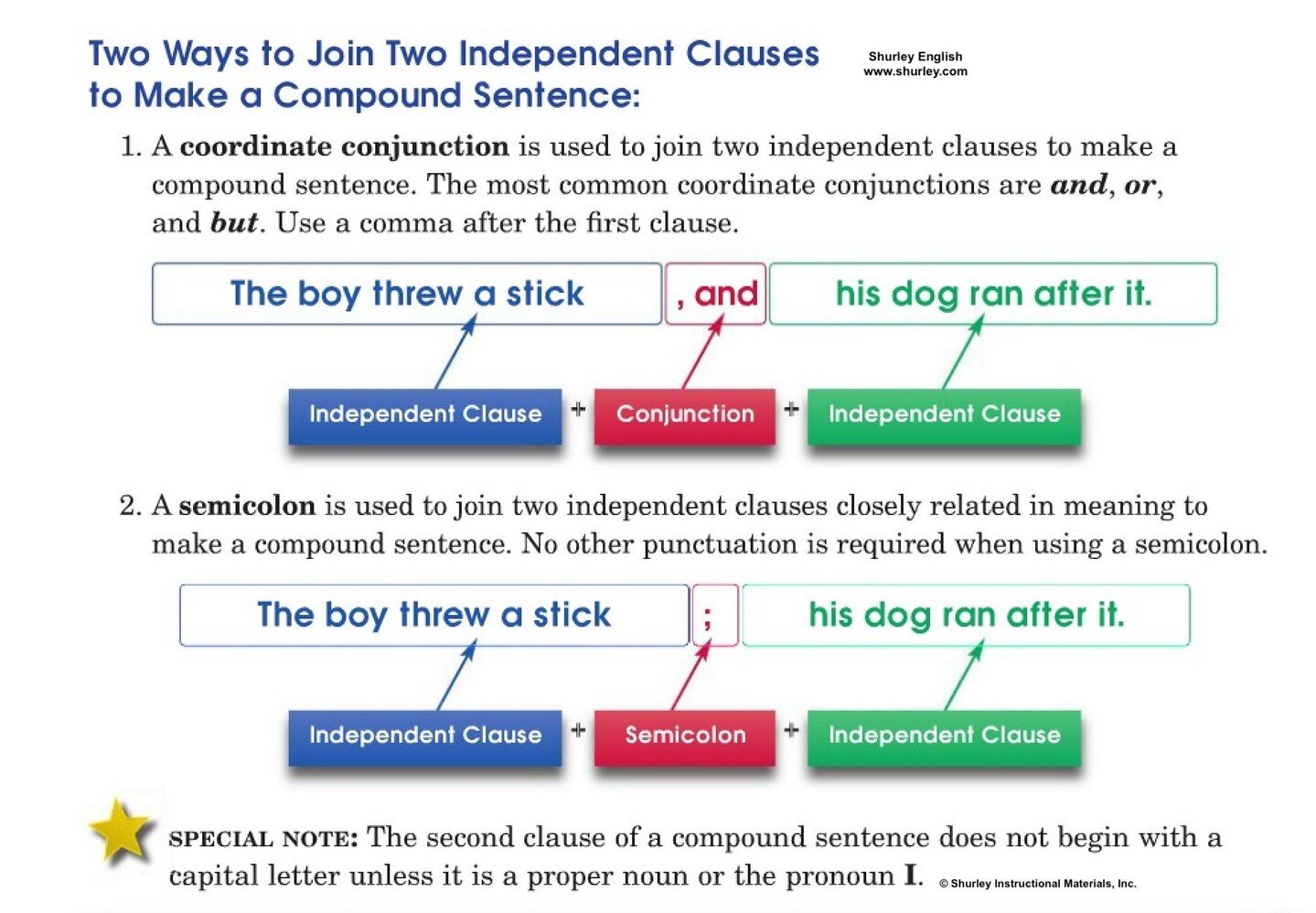
What are the different types of idioms?
It’s important to know that idioms are usually peculiar to a particular group of people (region, country, etc.), and they may be difficult for people from other parts of the world to comprehend. Also, non-native speakers of English often have a hard time understanding them at all.
Idioms can add real flair to students’ writing, so here is a Lexicon for different types of idioms to explore. Encourage your young scholars to use them as a word choice strategy!
Slang Expression: a type of language that consists of words and phrases that are regarded as very informal, are more common in speech than writing, and are typically restricted to a particular context or group of people.
Regional Expression: of or relating to a particular region, district, area, or part, as of a country; sectional; local.
Informal Expression: suitable to or characteristic of casual and familiar, but educated, speech or writing.
Cliché Expression: a trite, stereotyped expression; a sentence or phrase, usually expressing a popular or common thought or idea, which has lost originality, ingenuity, and impact by long overuse, as sadder but wiser, or strong as an ox.
Proverbial Phrase or a Proverbial Expression: a type of a conventional saying similar to proverbs and transmitted by oral tradition. The difference is that a proverb is a fixed expression, while a proverbial phrase permits alterations to fit the grammar of the context.
Extend the Lesson:
Did you know that William Shakespeare coined many of the idiomatic phrases we still use today? Take a look at the following list of idioms Shakespeare used in his plays. Look some of them up to understand their meaning. Also, try to use some of them in a sentence.